Peiying Zhao#,Chao Han#,Yaru Lu, Jichun Tian,Jianjie Bi,Zhiying Deng Qunging Wang*and Qian Xu*Fusar...
內(nèi)容摘要
Peiying Zhao#,Chao Han#,Yaru Lu, Jichun Tian,Jianjie Bi,Zhiying Deng
Qunging Wang*and Qian Xu*
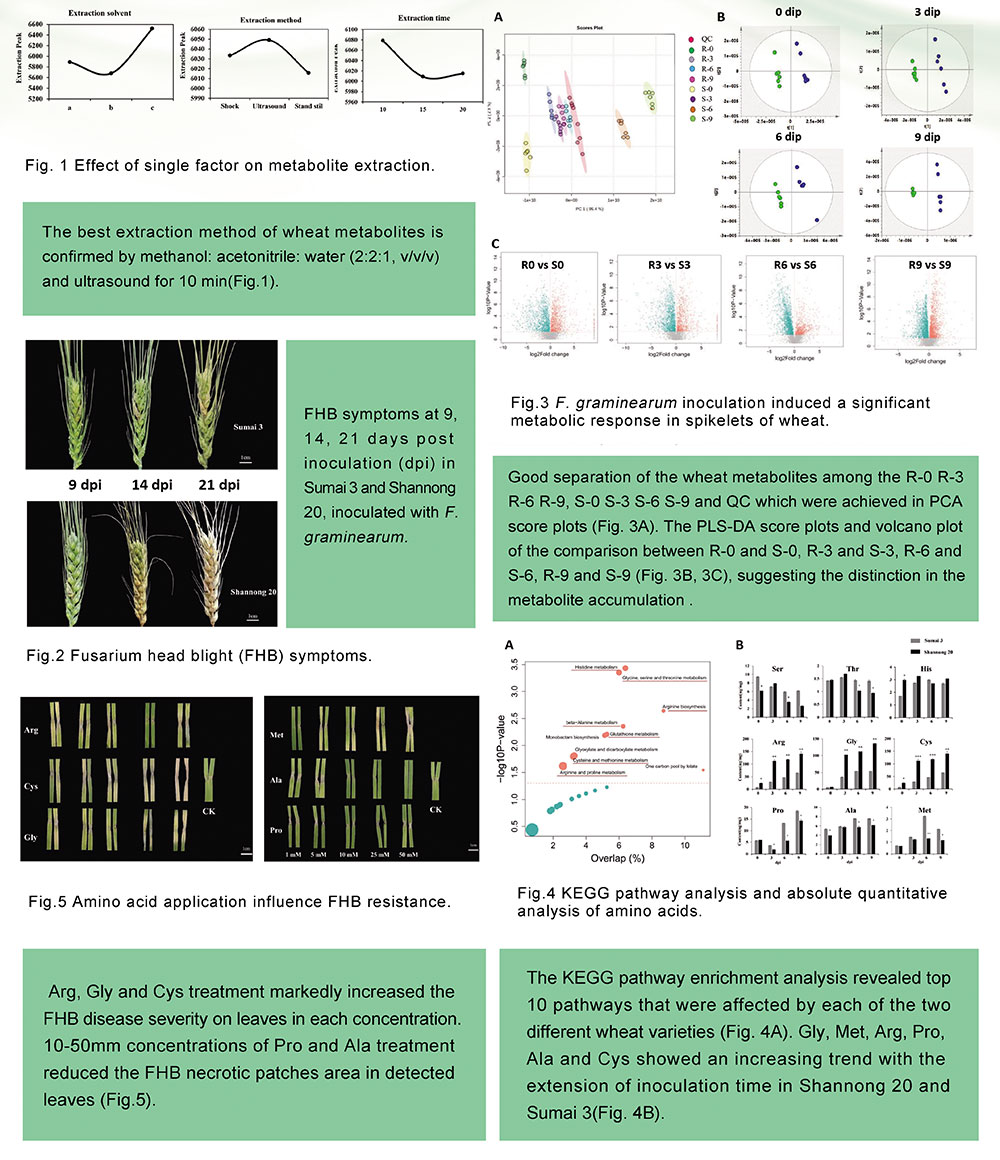
Fusarium head blight (FHB), a serious plant disease caused by Fusarium graminearum(F.graminearum),which severely reduces the wheat quality and yield. To clarify the resistance mechanism of wheat to FHB, untargeted and targeted metabolomics were used to analyze the metabolite differences of two wheat varieties the resistant genotype Sumai 3 and the susceptible genotype Shannong 20 after F.graminearum inoculation. The contents of Gly,Met,Arg,Pro,Ala and Cys in Sumai 3 and Shannong20 were increased with the time of F.graminearum infection by targeted metabolomics detection. Exogenous application of amino acids and F.graminearum inoculation assay showed that Pro and Ala increase wheat F. graminearum resistance, while Cys aggravate wheat severe F.graminearum susceptibility. This study provides initial insight into the metabolites of two wheat varieties . Moreover, the method of optimization metabolite extraction presents an effective and feasible strategy to explore the understanding of the mechanisms involved in the FHB resistance.
ZhaoP.Y.,HanC,LuY.R.,et al. Untargeted and targeted metabolomics profiling of wheat reveals amino acids increase resistance to Fusarium head blight.Frontiers in Plant Science,2021.(under review)


 技術(shù)支持:星際網(wǎng)絡(luò)
技術(shù)支持:星際網(wǎng)絡(luò)